Memory Training For Memory Improvement Enthusiasts
What you need is a trained brain. Memory training and the techniques you’ll learn with it will give you the tools that you can carry within your mind for the rest of your life.
Here on this page you’ll find all the training on “How To Memorise” so you can use them for your;
“Daily Life, Activities & Responsibilities”, “School & Education”, and “Business & Career”
as most of the techniques shared on my website will apply to all of these life activities.
Memory Training Course To Have A Trained Brain
Read, Learn, Prepare & Practice this detailed course on “How To Memorise” and you will develop a trained brain which will enable you to “Memorise & Remember Easily”;
Phone numbers | Dates | Passwords | Names & Faces | Public Speaking | Important Facts | Appointments | Birthdays | To Do Lists | Shopping lists | Exams | Math Formulas | Binary | Playing Cards | Languages | A Secret Language | Stunts |
And everything in between! Such as;
- Time management: Personal | Work | Home | Family | Finance | Yearly Goals.
- Calendar Memory: Techniques For All Activities.
- To Do List: List of jobs to be done created from the list above.
- Shopping List: for home, family and personal.
- Home DIY improvement list of activities | Repairs | New decoration | etc.
- Home management list: Bills | Utilities Management | Phone | Internet | etc.
- Car management: MOT | Tax | Repairs | Fuel | Insurance
- Health management: Dieting | Exercising | Weighing | Vitamins | etc.
- Doctor appointment dates
- Dentist appointment dates
- Holiday dates and activities
- Birthdays Of Important People
- Anniversaries
- Educational Studies & Activities
- Telephone Numbers: Personal | Business | Work | Family | Friends | Official | Other.
- Names and Faces – | Business | Work | Family | Friends | Official | Other.
- Visualisation Methods: Imagination, Association, 5 Senses, Action & Emotion.
- School: History | Maths | Binary | Important Names and Dates | Science | etc.
- Hobbies & Interests: Playing Cards | Images | Words | Numbers | Binary | Books
- Speech: Public Speaking, Father of the bride, Best man, and any other related speeches.
Ready to dive in and learn? Let’s start!
“How To Memorize”
A Crash Course On Your Journey
To A Trained Brain
Course Contents
Part One: Intro To Mnemonics & Memorising
* What is a mnemonic?
* What is memorising?
* How does the brain memorise the information?
* How to store the information in our memory?
* The Basics Of Memorising A Piece Of Information.
Part Two : 12 Mnemonic Tools & Methods You Need To Master To Memorise Everything
1. Storage & Retrieval: Memory Palace.
2. The Peg System & The Peg Method .
3. Acronyms.
4. Acrostics.
5. Chunking.
6. Grouping & Organizing.
7 . Linking Mastery: Pair Linking | Chain Linking | Top 5 Methods Of Link-Actions!
8. Number Shapes
9. Number Rhymes
10. The Story Method
11. Visualisation & Imagination
12. Spaced Repetition
Part Three: The Shaper System
* The Shaper System Starter Version – Free Full System Download.
* The Shaper System Full Versions – Free Full System Download.
Part One: Intro To Mnemonics & Memorising
What is a mnemonic?
A mnemonic is a tool that helps us to memorise a piece of information, and also reminds us of what we have memorised.
A mnemonic acts as a “Reminder Trigger” or a “Clue Trigger ” of what you have memorized so you can remember it by its clue. We often need a clue as a reminder of something we need to keep in mind or to remember. This is where the use of the mnemonics are awesome!
Simply put; A Mnemonic Reminder or A Clue is something that you already must know before you connect a new information data item that you are trying to memorise. In other words, you are connecting a pair of information with what you already know and with what you are trying to memorise as a pair-link.
Here is a quick example;
Let’s say we want to memorise to;
“pick up some fresh Eggs from the local farm.”
A Mnemonic you have to choose before you memorise the items.
Let’s say you choose your “Car” as the “Mnemonic-Clue-Reminder” as you might be driving to the farm.
Now let’s pair-link the reminder and the new information together.
Take a few seconds to Imagine yourself “driving your car to the farm, and filling up the back seat with full of Huge Eggs“.
There you have it. The Car and the Eggs are connected by pair-linking the two together. You have memorised a new piece of information item , the “Eggs” with the item you already know attached which is your “Car”.
You can then do this with many items on your list to memorise whatever they may be. This is the very basic of memorising a piece of information using mnemonics. We’ll get into more details about this in the following title as “The Peg method”.
To have a better memory than you have now, you need to understand each mnemonic tool with its uses. This will be the base towards having a trained brain, and to memorise anything you have the need to.
What is memorising?
Memorising is storing information within our mind, with the help of mnemonic tools.
But where in our mind?
It’s been said that the area for memorising and storing information is “the hippocampus area” of our brain.
How does the brain memorise the information?
The brain itself auto-records information throughout the day with an average of 60.000 thoughts with all the Actions & Emotions involved within those thoughts. We by default record all the events on that day, yesterday, a week ago, or even a few years ago. It’s because of all the habits, regular activities, and the responsibilities that we have in our lives that are made of of all actions & the emotions attached to them. This is “The Working Memory“. Our working memory is always recording everything for short or long term without making a lot of efforts.
How does our brain memorise when we purposefully want to memorise new information other than normal day to day activities?
The hippocampus area of the brain does not by default memorise or remember new information data that you want to commit to memory. We also need to create a storage area within our memory, so the new information can be placed into the storage area within our memory, our mind. This storage then can hold all the new information we want it to hold.
The storage is known as “The Memory Palace”. We also use other elements to store data such as “A Mini-Palace” which are the pegs of all kinds of items that can also have a lot of locations and can be used as mini-storages.
We know that we have to have a storage to memorise all information if we wanted to commit them to our memory. Simply because all information has to belong to a space somewhere, and within that space, the new information can be placed and stored.
How to store the information in our memory?
Our brain works by seeing animated-images before it can commit that information to memory.
The Basics Of Memorising A Piece Of Information is to mentally prepare;
- A Memory Palace with enough locations based on what you need to place into the locations.
- Organize the information you want to memorise so they would fit into the locations of your memory palace. So if you have 10 items to memorise, you’d need 10 locations in your palace.
- Associate and Convert each information into an image, and mentally place that image into the memory palace.
- Revisit your memory palace’s locations to retrieve the information you have placed in them.
Here are the 12 Mnemonic Tools & Methods You Need To Master To Memorise Everything
These tools will give you many ideas and insights, techniques and methods that you can use immediately to memorise a list of items, facts, numbers, words, names, procedures, and even a speech! Possibilities are limitless.
1. STORAGE & RETRIEVAL: MEMORY PALACE
A Memory Palace is a “Mental Storage Space” to save the information you want to memorise, and to retrieve the information once it’s memorised. This is mostly how we memorise information either short or long term.
A Memory Palace can be any building, as long as you can choose locations within that building. When you have a building that you want to use as a Memory Palace, Make sure to Memorise Your Memory Palace as all memorisation takes place in your mind.
And once you have those locations in your memory palace, you simply add the information you want to memorise into each location by way the available choices of;
* Simply adding or placing the information-data item into that location. Make it belong there.
* Using the existing item on a location, and Pair-Linking the existing item with the information you want to memorise together, to strengthen the scene.
* Pair Linking two items together and placing them into the location.
* Chain-Linking a few items together and placing them into the location.
A Memory palace has to be pre-organized, based on what you want to memorise.
All memorisation takes place in your mind. You store the information, and you recall the information, all within your mind. To help you to do this, we use a Memory Palace. We store the information in a memory palace, and all we have to do is to walk back mentally to see what’s in the store, or your memory palace.
Memory Palace is also known as “The Method Of Loci”, or “The Journey Method” which suggest a path to walk through a palace, a building you know well.
The Method Of Using Your Memory Palace is by choosing a building such as your home, and choosing the rooms in your building, and then choosing the Trigger Locations & the Items within those rooms.
How To Set Up And Memorise Your “Memory Palace Storage”
- Choose a place that you know very well such as your Home, or office, school, bank etc..
- Walk all the rooms, get to know each room inside out.
- Identify 5 Locations that holds 5 different items within each room.
- Remember that each 5 item in each room will be your “Permanent Items”.
- Commit all the rooms onto your mind. Memorise your palace!
- Walk your palace mentally over and over until it’s printed in your mind.
- Make sure to mentally see all 5 items in each location for each room.
- Count out loud the first 5 items in the first room by pointing your index finger to each item. So when you are standing at the entry of the room, you would count out loud and say “1-Bed” pointing your index finger, then say 2-Table, 3- Mirror, 4-Chair, 5-Shoes. This would be in your first room. Memorise your first room with all 5 stops, and the 5 items at those stops.
- Go to the next room, again count out loud 6-Monitor, 7-Bookshelf, 8-Small-Bin, 9- Glasses, 10-Bag. So your second room holds the locations and the items from 6-10.
- Repeat this process for all the rooms in your memory palace. So If you have 5 rooms, your last count would be 25-and-the-item-name.
- Keep a written copy of the memory palace. Draw and Or Write it down and store it away.
- Use spaced repetition to revisit the palace from your written copy, repeat the walk mentally.
2. THE PEG SYSTEM & THE PEG METHOD
The peg method is an alternative method for a memory palace. It’s a quick way of memorising a short-list of items attached or hooked with a pair-link to the items known as a pegs.
The peg method works by pre-memorised items that are used as hooks to attach the new information by way of pair linking an action between the two.
Remember you have paired a link between your “Car” and “Eggs” before?
What you have done is Pair-Linked a Peg item which is your “Car” which is the item that is pre-memorised, with the new item “Eggs”.
That’s basically what the peg method is. You attach new information to an item that you already know as a Pair-Link.
The peg method is also a very powerful method for memorising a list of items that really don’t have the need for a memory palace. Although using a memory palace with your paired-peg-links will strengthen the scene and will be more memorable, the peg method does not rely or depend on a memory palace so you can memorise your list without the need of creating a memory palace.
A peg can be any tangible item. A peg can be your hands, can be your car, your TV, it can be any item that you have as a list that can be used to attach new information.
Popular Pegs that can be pre-memorised to be used anytime you have the need to.
Using the peg list below are what you need to prepare for yourself to memorise any short or long list of items.
Find images for each list. Practice memorising your lists. And use them whenever you have a list of information you want to memorise, without the need of a memory palace.
It’ll be worth it!
THE PEG PALACE
Here are some Peg-Lists ideas you can use for your Peg-Palace.
Alphabet Pegs. A-Z Each with 26 Items.
26 Items Per Alphabet Pegs. With each letter representing a tangible item. Such as;
* Alphabet Animals: Animals that start with the alphabet letters. 26 pegs.
* Alphabet Fruits: Fruit names that starts with each letter. A: Apple B: Banana .. 26 pegs.
* Alphabet NATO: A: Alpha, B: Bravo, C: Charlie .. 26 pegs.
* Alphabet Persons: Person names that starts with alphabet letters. 26 pegs.
* Alphabet Shapes. Items that looks like the objects. 26 pegs.
* Alphabet Sounds: A-Ape, B-Bee, C-Sea .. 26 pegs.
A Total of 156 Alphabet pegs.
Number Digit Pegs
* Basic 0-9 Number shapes. Gives 10 items you can use as hooks or pegs.
* Number Rhymes Pegs: I have listed 30 Items you can use as pegs.
* The Shaper System Images as Pegs from 00-99. Gives you 100 Pegs!
* Major System Pegs 00-99: Items that are made of words using the phonetic sounds. 100 Pegs.
A Total of 240 Number-Digit pegs.
Everyday Objects Pegs
* Colour Pegs: 10 Pegs. Choose 10 Colours and use them as pegs. Such as “Red-Car” as a Pair-Link. You can simply use the colours to link with your list with whatever you want to memorise.
* Musical Instruments: Choose 10 music instruments, find images you can use which will give you another 10 pegs.
* School Items: Choose 10 items that you would take with you if you went to a school, find images you can use which will give you 10 pegs.
* Planets: If you have memorised all 10 planets already, why not use them as the next 10 pegs.
* Market/s: Choose 10 items that you always buy which gives you 10 more pegs.
* Car: Choose 10 item-spots around your favorite car. Gives you 10 more pegs.
* Office: Choose at least 10 office items. 10 more pegs.
A Total of 70 Everyday Objects pegs.
Persons & Body Pegs
Your Body: Choose 10 spots on your body and you have another 10 pegs, such as;
Hair | Eyes | Nose | Mouth | Chin | Neck | Chest | Stomach | Legs | Feet.
10 More pegs here using your body.
Other People’s Body
Remember you have a list of 26 people in alphabetical order?
Why not use each body with 10 spots as above?
Perhaps you may even use their unique clothing as pegs as well.
And you have another 260 pegs!
A Grand Total Of: 736 Pegs for your Peg-Palace!
Using Pegs with the linking method
With the linking method, we use the pegs with;
- Familiar (pegs) + Familiar (pegs) such as memorising number digits.
- Familiar + Unfamiliar (not pre-memorised and new) such as attaching words/objects.
- Unfamiliar + Unfamiliar, two items not pre-memorised pair-linked by an action.
One of the examples for Familiar + Unfamiliar is learning a foreign word where we attach an unknown word to a known word.
With the Link method, we can use pegs and apply an action involving the two, or more. We can use pre-memorised pegs, and or unfamiliar objects with other objects, which can then be either attached to a pre-memorised peg, or at a spot in your memory palace.
I mostly use the memory palace method, because even if I use the peg system, I still have to place the linked image onto a location, and he scene becomes much more memorable. However, the peg method is great for a short and or a long list of information and can used at anytime and at any situation. Simply pair link your pegs with the images that represent the information you want to memorise. Many stage performers uses the Peg Method to memorise their speech, jokes, stories, facts and other data as it’s still a very popular easy method. It’s worth mastering this brilliant mnemonic tool.
Pegs for short term memory
Reusing your pegs on the same hour or the same day may give you ghost images.
I would not use the same pegs twice in a day for two different list.
Wait at least a day before you use the same pegs again for your next list of items.
A to-do list, shopping list, or any daily list can be memorised using the same pegs everyday.
You can memorise a few different lists using a few different Peg-List everyday.
So you might have a To-Do list, Shopping-List, Work-List.
Simply assign a Peg-List to each one of your lists.
And memorise your new list of items using the same peg list everyday.
It works well.
I have 50 items in my little office I use as pegs. I memorised them in a numbered order, so I can go from the first item to the next without any confusion. And memorise a huge list, or a few different list when I split it into the amount of locations I need each day. So in a way my office is another memory palace made up of 50 pegs. That’s how I construct my memory palaces. I always have the objects I either know they are there, or I simply place them there myself.
Pegs for long term memory
You can still use your Peg-List for long term memory. It would just mean that you cannot reuse those pegs again, because you would have your information linked to those pegs permanently. So your pegs becomes permanent pegs, and so does the info attached to those pegs.
I use number shapes, alphabet objects, my body, my-car, musical instruments, office items, and some other everyday objects as Pegs-Storage.
No need to create a memory palace storage if you have a good few Peg-Lists.
The idea would be to create more Peg-Lists if you have a lot of long term information you want to memorize.
Memory palace is always the best friend for long term memory.
As mentioned before, I still use my memory palaces to place my pegs along the journey. It becomes an expandable palace. It becomes very memorable, it’s almost never easy to forget!
3. ACRONYMS
Acronym is a made up word that are made of the first letter of other words.
Acronyms helps us remember a list of words compressed into a single word.
Here are some examples;
JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group
NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization
BBC: British Broadcasting Corporation
ROY G BIV: Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet (Rainbow Colours)
Many public speakers uses this simple acronym model to give speeches for an hour or even longer. Here is an example;
SUCCESS: See your goal | Understand the obstacles | Create a positive mental picture | Clear your mind of self doubt | Embrace the challenge | Stay on track | Shake The World.
4. ACROSTICS
Acrostics are words that forms a sentence like phrases or quotes, or poems. It’s almost the same as an acronym, we still use the first letter of each words, except we create words in replacement of the original list of words.
Here are some examples;
The order of the planets in the solar system.
Original Words:
Sun | Mercury | Venus | Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune | Pluto
Acrostic Words:
“See My Very Easy Method Just Speeds Up Naming Planets”
The order of algebraic equations
Original Words:
Parenthesis | Exponents | Multiplication | Division | Addition | Subtraction
Acrostic Words: (PEMDAS)
“Please Excuse My Dirty Aunt Sandra”
5. CHUNKING
Try memorising this; 2158956970
Or this; tbghsytdpy
Not easy for most people. However, if I now separate them into two part chunks this is what we would get instead.
Now try it again: 21 58 95 69 70
and this one: tb gh sy td py
Would you agree that the second ones are easier to see, read, and helps remember easier?
That’s exactly what chunking is. We separate the data into smaller chunks because our brain can handle it much better in bitesize.
And we use those chunks to either pair link, or chain link them together to create a memorable story, mentally placed on our memory palaces.
For example; When we memorise numbers, it’s much easier to divide them into two or three digits chunks such as “00 15” , or “125 895”.
Make sure to always chunk your information into smaller parts each time you want to memorise a list.
6. GROUPING & ORGANIZING
If you have a lot of “random” information to memorise, then you may need to organize them into smaller groups.
For example you can separate your clothing lists, shopping lists, to do list, so they are all in their own groups lists. You can also group a category into its own groups.
Organizing the outline of any list will help you plan your memory palace and the amount of locations needed within your palace.
Always take your time to think of the systems and the methods you will use first. Next, choose or create a new palace for it with enough locations.
The rest will be to simply practice attaching the information to your memory palace.
7. LINKING MASTERY: “PAIR” AND “CHAIN LINKING”, + Top 5 Methods Of Link-Actions!
PAIR LINKING: We remember better when we connect one piece of information with another piece of information. This is known as “Pair-Link”. We link one item with another to make a connection between the two.
When we Pair Link two items together mentally, we create a mini-story or a scene from the outcome of the link. These link could be objects and objects, Persons & Person, Person and Objects. It can be any type of link as long as you can link both together via a story.
CHAIN LINKING: You have probably guessed it already. Chain-Linking is connecting more than two items one after another. So if you have a list of 10 items to memorise you can easily connect them together by a continuous story. And you would of course again make this happen on a location within your memory palace if you want this to be in your long term memory.
Here is an example for “Pair-Linking and Chain-Linking” by also using the “Mini Story Method” with a starting location on a memory palace;
Let’s say we want to memorise this “To-Do List”.
9 am: Buy Fuel for the car
10 am: Call Dad
11 am: Library
12 pm: Pay the bill
13 pm: Swim
14 pm: Pick up groceries
15 pm: Car Wash
Let’s start with the location first.
Since this list starts with buying fuel for the car,
we can think of the starting location as “The local Fuel Station”.
* Now imagine you are;
“at the fuel station“, and you are “fueling your car“, and your “dad calls you on your phone“.
You have just Pair-Linked “Fuel & Dad” together.
Location: at the fuel station
First Item in the pair: fueling your car
Second Item in the pair: dad calls you on your phone
Now Let’s Chain-Link Them Together By Adding The Time Element to the list.
* To remind you of the time which 9 am & 10 am for both links;
First way is to use number shape images as pegs-storage, so we can also link them into the story.
The number digit “9” is the shape of a Balloon, number “10” is a “Stick & Drum”.
So now we use a “Balloon” and “”Stick & Drum” as a peg-storage to remind us of the time for it as well as the mini-story which the paired-link for “Fuel & Dad”.
Now the story changes into “Location” + “Time-Link” + “Chain-Link” = Mini-Story.
“You are at “The Local Fuel Station” + “A Balloon is tied up the fuel cap” + “you open cap with the balloon stuck to it, and start fueling your car“.
and your “dad calls you on your camera phone” + wearing a “Huge Drum Stuck On His Head.
You have now created a Chain-Link and produced a “Mini-Story” using a memory palace location, and a peg to store the time.
Let’s analyze the chain-link here;
You have used a single location, and placed a chain-linked mini-story for the first Two-Items with their corresponding times.
Location: at the fuel station
First Item in the pair: fueling your car
First Peg-Storage Item: Balloon for digit number “9”
Second Item in the pair: dad calls you on your phone
Second Peg-Storage Item: Drum for digit number “10”
This is exactly how we mentally pair and chain link to create a mini-story, and store them at the mental location we have chosen, either on the spot, or at a pre-memorised memory palace.
Person Object Paired-Link
One other way to memorise this is to use PO: Persons, Objects, and action-links.
Let’s say you have 100 persons from 00-99.
Your 09 would be a person who would represent “09 am”.
Let’s say your 09 Person was Superman;
Your story would look something like this;
“Superman is at The Local Fuel Station, Fuelling The car, while talking to his Dad on the phone who is wearing a huge drum on his head”.
Location: Fuel Station: “Memory Palace”
09 am: Superman: “Person”
Fuelling The Car: 2 Items or “Objects”
Pair-linked: by an “Action” -> “While talking to his Dad on the phone” “who is wearing a huge drum on his head.”
It takes a lot of lines of text to explain how the whole thing works, but as you can see it’s just a matter of practice to memorise all of this information within a matter of a few seconds at a time.
When you practice these skills, you’ll notice yourself getting better and faster at creating pair and chain links, and having lots of fun with it!
Now let’s move on to the rest of the list by chain-linking them together to give you some more ideas;
When your Dad calls you, he tells you that he is waiting for you at the local library. Now you have just linked “Library” to “Dad” which creates the first chain-link.
Now we will connect Library to Bills to continue with the chain-linking.
You arrive at the library, goto the desk, and Pay the bill to the Librarian at the desk. Imagine yourself walking in and start paying the bill at the reception inside the library.
Let’s now connect “Bills” with “Swimming”.
As you pay the bill, you notice the library’s floor is flooded with water rising up to chest level. You start “Swimming” out from the building.
Let’s now connect “Swimming” with “Groceries”.
As you swim out of the library building, you notice a lot of groceries floating around, and you simply pick them up and bag them up.
Let’s now connect “Groceries” with “Car-Wash”.
Let’s go crazy this time, and let’s wash the car with the groceries you have just picked up!
As you can see, you simply connect two items together, and then create the next 2 by using the previous and next by chain-linking them together. And by doing so, you are creating a crazy story that may just take you a couple of minutes to think and to mentally visualise, but will stay with you to remember for the rest of the day!
As for connecting the times with your To-Do List, or any list, you would need a number system as explained above, so that you can also connect them into your Paired-and-Chained-Links. There a few “Number To Image Generator” systems. I use The Shaper System as my own number to image generation which are all pre made so it’s always available to use as and when I have the need to. It’s available for you to download and use all the images I have already prepared for the shaper system, one of which is the Starter Version, the other is the Full version.
Both are available to download for Free! A “Thank You Prayer” is all I want in return, knowing that I have also helped others with their goals.
Pair-Linking with Memory Palace Only
You can also use the same list to memorise without a chain-link. This is where we use a memory palace for all the paired links.
Here’s how you’d do it using one of your “Memory Palace Storage“.
Choose a memory palace. Pair-Link the first 2 items together with Fuel & Dad, and place that scene onto the first Trigger Location in your memory palace.
Next you pair-link “Library & Bills” and place that onto the next Trigger Location in your memory palace.
And repeat this process with as many paired-links as needed! Use pegs-storage items where it is necessary inside your memory palace.
Top 5 Action-Methods Of Pair-Linking and Chain Linking!
Follow these tips, methods and insights, and put in the practice, and you’ll never run out of actions and imaginations!
When we pair link two bits of information, we create actions between the first and the second item by way our imagination. However, it’s not always easy to find an action when we link items together such as “Toothbrush” and “Spaceship”. They have no logical connection to each other. It can be a struggle to find an action to link them together.
This is where the top 5 methods of linking comes in handy to learn, remember, and to apply.
1. “Mini & Mighty” Link Method
This is where you make your objects mentally shrink or enlarge by way of an action. It’s a very fast method to apply. Read on…
Let’s pair link these 2 items for our example;
“Airplane” & “Pen”.
A quick reminder of Words to Images System
Each time you have words, associate and convert them into images. And each time you convert them into images, go through the questions below;
(Make sure to Also master the Visualisation & Imagination section!)
What type of object is it? What type of Airplane is it?
What does it look like? What does this type of airplane look like?
What does it sound like? What sounds does it have when it works or does something?
What does it remind you of? Does it remind you of another object, person, place?
What colour is it? Is it one colour? Or a few mixture of colours?
What size is it? How big would you say this Airplane is?
Now do the same with the Pen.
Let’s now do our example of Shrink Or Enlarge or “Mini” & Mighty” using the two items to pair-link them.
Imagine looking out of your kitchen window, and seeing a Mighty Big Airplane flying towards you, and it gets smaller and smaller, and fits through the window, and lands on your table in the kitchen. And on the table you have this Huge Pen as big as the Table. You pick up the huge pen, and push the length of it through the airplane. It looks like a Pen with Airplane wings!
Mentally shrink the item into a “Mini-Object”, and where necessary, make the item “Mighty Big Object”.
This will immediately give you the size to work with your actions.
2. “Morphing & Transforming” Link Method
This is where you make your objects mentally morphing into, or transform into another object. So it becomes the object. It’s also a very fast method to apply. Read on…
Let’s go back to the “Airplane”, and “Pen” example to do this.
Remember the pen was pushed through the airplane? And it looked like a Pen with Airplane Wings? We already have applied a part of the transform method to the airplane.
To fully apply this method, you would first start with the Airplane on your table, and then mentally turn into the Pen. So you end up with the Pen as the last object. But the story would always stick as the transforming method is also a powerful Pair-Linking Tool.
3. “The Multiplier” Link Method
This is where you make your objects mentally multiply in 100s, one after another. Make them come out in many multiples. Let them fly, drop, hit things, add other actions. It’s one of the most fastest & effective method to apply.
4. “The Superhero Powers” Link Method
This is where you make your Objects or People have Superhero Powers. It works on a great level as it is very easy & fast to apply it.
Let’s take the number digits for “46” which is the “Seahorse” in the shaper system.
Now a Seahorse doesn’t really give us much to work with as its natural move is very basic. So now here we can give him a Superhero Power to have either a set action, or to simply give it a quick action for a quick memorisation.
Now imagine A Seahorse that has the power of Superman with Laser-Eyes! It Laser Burns everything in front of it!
How many Superheros with their individual powers do you know? Make a list of all of those powers, and memorise them. Use them when you pair-link your objects, or persons.
5. “The Clue-Shape” Link Method
This is where you “Add your Objects A Clue” so that it would act as another reminder that can be recognised instantly. It works on a great level. Requires a pre-memorised list of clues.
Add any type of clue possible. Use Colours, Shapes, Images, Pegs, Logos, Signs, Anything that would remind you of the item, or the next paired item in the list.
In the starter version of the shaper system, I have demonstrated the Clue-Shape Method with the images and its animations with a 1 Digit Number Shape System.
Adding Actions To Your Objects & Your Persons for PA or PAO.
Here is A list of Premade Actions you can use to create your Pair, and Chain-Links along with the top 5 methods of using them together.
- acting
- animating
- attacking
- arm-wrestling
- applauding
- blowing
- balancing
- balancing (self)
- bandages
- bangs
- barking
- bathing
- begging
- bending (object)
- bends (over)
- bicep curls
- biting
- bouncing
- bowing
- breathing
- building
- burning
- burping
- buying
- carrying
- chasing
- checking
- choosing
- clacking
- climbing
- coming
- commanding
- conducting
- conjuring
- cooking
- coughing
- cracking
- crashing
- crossing
- crushing
- crying
- cutting
- dancing
- delivering
- digging
- diving
- drawing
- dreaming
- drinking
- driving
- drooling
- dropping
- dunking
- eating
- eating
- electrocuting
- enlarging
- exploding
- fainting
- falls
- farting
- faxes
- feeds
- fights
- fist pump
- flies
- flips
- flirting
- floats
- flying
- gazes
- give
- goes
- goes into labour
- grabs
- gurgles
- glued
- halts
- handstands
- hangs
- harpoons
- hiccups
- hides
- hitting
- holding
- holds
- howls
- hugs
- hyperventilates
- identifies
- inspecting
- into
- jails
- juggling
- jump shot
- jumping over
- jumps
- kicking
- kicks
- kisses
- kissing
- knocks
- laughs
- levitates
- licking
- licks
- limps
- lunges
- makes
- marches
- meditates
- milks
- mining
- mixes
- moonwalks
- mouth to mouth
- nets
- opens
- paints
- pecks
- peels
- picks nose
- pierces
- piloting
- pinches
- pirouettes
- places
- plays
- points
- pounds with fist
- prances
- praying
- prays
- pretends to be
- puckers cheeks
- pulls
- pulsates
- pushes
- punching
- pouring
- rains
- raises
- regenerates
- removes
- repairs
- rescues
- rides
- rolling
- rubbing
- rubs
- running
- runs
- sails
- salts
- salutes
- saws
- scat singing
- scratches
- screams
- shake
- shaves
- shits
- shivers
- shoots
- shuffles (cards)
- shuffles
- sings
- sips
- sits
- sitting on toilet
- skipping
- sleeps
- smokes
- smelling
- smiles
- smokes
- sneezes
- sparkles
- spiking
- spits
- squeezes
- staggers
- stepping on
- stops
- strangles
- stretching
- strums
- stuffs
- sucks
- sweeps
- swims
- swing
- takes
- talks
- throws
- tackles
- tickles
- ties
- touches
- turn
- turns
- urinates
- uses
- walk
- wants
- warms
- washes
- washing
- wave
- whistles
- whines
- whips
- wink
- wishes
- wont
- wraps
- wrestles
- writing
- yawns
- yodels
8. NUMBER SHAPES
Number shapes are images that looks like number digits. As an example; Number digit “0” looks like an “Egg”, or a “Ball”, “Hula Hoop”. It can be any object you like as long as it’s a lookalike shaped object.
We use number shapes as “pegs”, which are the objects that we use as a storage which is an alternative way of using a memory palace, and as part of a Number To Image Generating System. You can in fact use a memory palace with pegs which would in fact make the Paired-Links much easier to memorise for long term. To memorise a quick list of items, number shapes are the perfect and probably the faster way of memorising almost any short list you like, and remembering for the rest of the day with ease.
The idea of using Number Shapes is to memorise information by pair-linking them together.
Here are first the Number Shapes from 0-10 which would allow you to memorise a list of 11 items. Or more than 11 items if a story method is used as explained in Chain-Linking.
0 Egg
1 Wand
2 Swan
3 Butterfly
4 Chair
5 Unicycle
6 Golf-Club
7 Boomerang
8 Snowman
9 Balloon
10 Stick & Drum
Here are the images for Number Shapes from 0-10
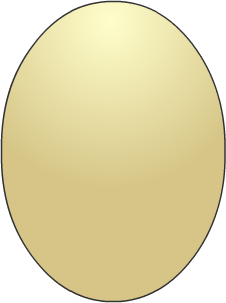
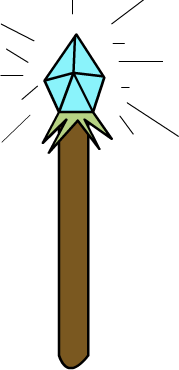


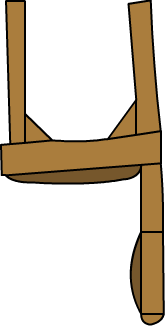
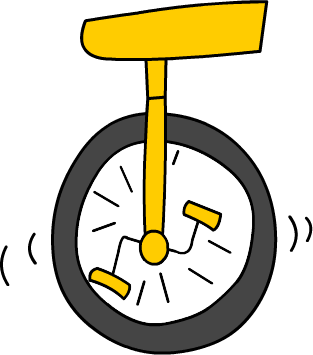



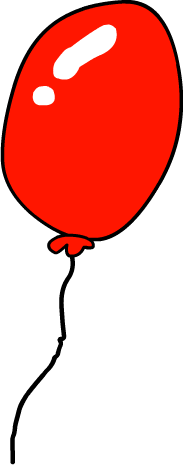
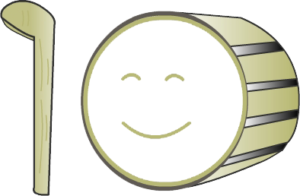
Here is an example of how you’d use the basic number shapes to memorise a quick list.
Remember we had a “To-Do List”? Let’s use the same list but this time using the Number Shapes as the storage for the list.
We have;
9am: Buy Fuel for the car
9.30am: Call Dad
10am: Library
10.30am: Pay the bill
11am: Swim
12pm: Pick up groceries
1pm: Car Wash
Let’s start with the digit “0” as the first number shape item which is an Egg.
Now let’s Pair-Link “The Egg with Fuelling The car”
Imagine yourself with some eggs in your hand, and you are fuelling the car with those eggs!
You have now Paired the Link with The Egg and Fuel together. As you can see here there is not a need for a memory palace because we are simply using number shape items as a storage for what we wanted to memorise. You can of course also use a memory palace to place your Paired-Links into the Trigger Locations which would also make it much more memorable. However,the idea of using pegs such as Number Shapes is so that you can quickly memorise a list without needing a memory palace.
Now let’s connect the next item in the list which is to “Call Dad”.
The next number shape we’ll use is digit “1” which is the “Magic Wand” object.
Imagine that you have a “Magic Wand” in your hand this time, and waving it and tapping the air, and making a your Dad appear in front of you, and at the same time hearing the phone.
Next is the Swan, the number shape for “2”. The item we need to memorise in order is Library next.
Imagine a Huge Swan running around the Library and pecking into all the shelves and the books!
Got the idea? Great! I’ll let you practice with the rest of the items using the rest of the number shapes.
9. NUMBER RHYMES
Number Rhymes are images that sounds and rhymes like number digits which are also used as pegs, which means they are also a storage mnemonic tool to memorise a list of items.
The use of the Number Rhymes works the same way as the number shapes when we want to memorise a quick list of items. It’s also a very popular method used by a lot of public speakers, actors and stage performers alike.
Here is the basic 0-10 Number Rhymes that you can use to memorise a quick list for your needs.
0 Hero
1 Wand
2 Shoe
3 Tree
4 Door
5 Hive
6 Sticks
7 Heaven
8 Skate
9 Shine
10 Hen











And here are the next 20 Number Rhymes I have created a while ago which may be handy for a long list memorisation.
11 Elephant
12 Elves
13 Typing
14 Fountain
15 Fighting
16 Sardines
17 Surfing
18 A Tin
19 Noting
20 Twin
21 Chihuahua
22 Twitter
23 Trophy
24 Tofu
25 Truffles
26 Twix
27 Tweezers
28 Terminate
29 Tasty-Wine
30 Thirsty




















Can you contribute to the rest of the Number Rhymes from 30 onwards? And would like me to share and update it on this page to help others? Send me an email with your list and I’ll update your list here with your name as the “Contributor”.
10. STORY METHOD
We humans love stories. One of the simple reasons why we love stories is because our brain is naturally programmed to remember stories. Our brain has the ability to see animated images that forms the story. Just like a movie.
This method is also used for memorising words, quotes, and text-books.
A story can be a short story like a “Mini-Story“, or as long as you can make it like a “Long-Story“.
A mini story is created by a “Paired-Link“, and longer stories are created by “Chained-Links“.
Here is a quick example of a Paired-Link for A Mini-Story.
Let’s say we have to memorise the following;
Egg | Shoes | Car | Book
Let’s Pair-Link the Egg & Shoes for the mini story.
Imagine “you are cracking a huge Egg on your Shoes.”
There you have it. You have just created a Mini-Story by Pair-Linking the first two items.
Now let’s create a longer story by Chain-Linking the rest of the items or words.
Next is the Car. So we will link “Shoes” which was the previous item, with the next item “Car”.
Imagine “you are taking off your Shoes, and start hitting your Car with it”.
Next in the chain is the “Book”. So we’ll now link the previous item which is the “Car”, with the next item which is the “Book”.
Imagine “you are pulling a huge Book out of your Car”.
And there you have it. Pair and Chain Linking is how you create a story withy the information you have in your hand. With this method you can literally memorise almost anything you like!
Give it A Start Location OR A Memory Palace
Single Location Start: The example story above starts with you cracking an egg on your shoes. However, you still have to give this story a location to start with so you know where this happens. As it is “you” in this story, you have to exist somewhere. Where are you? Are you in the kitchen, garden, in a park, museum? Where are you? What is the starting location for your story?
You can create your story from a single location, and simply extend that location by adding your chain-links into your story.
Memory Palace: The other method would be to use a Memory Palace. Simply place Paired-Links or Chain-Links into each location in your memory palace.
11. VISUALISATION & IMAGINATION
We know that our brain sees animated images just like a movie before it can record or store the information we want to memorise, therefore improving visualisation is probably one of the most important part of having a trained brain.
The good news is that Visualisation is a skill you can learn! It’s just like a learning any other skill. The more you do it the better you’ll get at it. Just like riding a bicycle, you fall, fall, and then balance, and pedal away. It’s a skill that can be learned with the knowledge available, and the practice you put into it.
You get better and better with it as you practice more and more at it. I had one of the worst ever memory when I first started my journey in the art of memorising. With the knowledge and practice, you will develop to be at least 500% or more better than ever before. As for myself I am 1000% better as I have now been practicing for many years and it has now become a second nature to me. It will be with you as well as long as you put some practice into it.
FOCUS: Deciding to remember.
Basic understanding of “How to remember and recall what you have memorised” is first to “Decide To Memorise It”.
First, you need to decide that you want to remember, and that you have a desire to memorise that piece of information. This will activate and force your brain to think, focused more and take action. But if you don’t decide to remember it in the first place, then you will simply forget it because the brain did not care enough to remember it therefore it sees it as a low value information. So make a decision to decide to remember what you are going to memorise, be it a birthday, a daily to do list, work related, educational, personal, a speech, or whatever it may be.
To remember it, you have to memorise it.
This is at its most basic, and it is that you first have to decide to memorise whatever it is you want to memorise so that you can remember whatever it is you want to remember.
You cannot remember anything if you have not memorised it already.
If something new has not happened, you would not have a recollection of it. There would be nothing to remember.
To be able to recall what you memorise will first require you to really understand how it works and then practice until it becomes a second nature. And yes it does become a second nature as all the memory people will tell you that you’ll be developing a better and stronger brain that will have the ability to memorise and recall anything you want.
Exercising your brain is like exercising your body, what happens if you lift weights 50 times a day for a month? You will notice that your muscles are getting bigger and stronger, and this is the same with your brain. By applying memory techniques, you’ll notice that your brain will get also get better, faster, stronger and more able to solve issues.
How To Improve Visualisation:
Ask each time you associate an image to an item or a piece of information, be it an object, a name, words, number etc. ;
* What does it look like?
* What does it sound like?
* What does it remind me of?
There are 5 Main elements to visualising & imagination.
1. Using Our 5 Senses
2. Associations To Generate Images
3. Using Exaggerated Actions
4. Using Exaggerated Emotions
5. Remember To Practice
1. Using Our 5 Senses
Let’s start activating your imagination.
Observation: Eyes
Our eyes are tools to seeing everything. The reality is that we see everything with our mind’s eyes.
Follow this exercise: Look at what’s in front of you. Wave your hands over what’s in front of you. Notice at least 3 everyday items that is in front of you.
Now close your eyes, and try to see with your mind’s eye what you just did. Did you recall what you just did? Were you able to see what you did with your eyes closed?
Great. You have a wonderful memory! A memory that can be trained to memorise anything you like.
- Colour: Now do the same action again, but this time, have a look at the colours of what’s in front of you. May be there are some items there that are red, blue, yellow, or some of them are a mixture of colours? Notice what they are.
- Shape: Next, have a look at the shapes of those in front of you. Notice their outline shape, and how they look like?
- Size: Next, notice the size of those items in front of you, how big are they? how would you describe it?
Sound: Ears
Are any of the items in front you has any sounds by default? Do you have to cause an action to hear the sound of an item in front of you? How do they sound like?
Aromas: Smell
How do those items smell? Can you recognise the smell of any of those items. How do they smell like?
Feel It: Touch
Touch the items. What does the material feel like? Soft, hard, metal, plastic, leather, wood? If you were to lift it, how heave is it? What’s its weight?
Flavours: Taste
Are any of these items eatable? If you were to take a bite into each item, what would they taste like? Can you compare it with any type of food, or drink or any other tastes?
2. Associations To Generate Images
Whenever you have the need to memorise a piece of information, you must find an image for it. Simply put; “A Tangible Item” that you can use to pair-link with either your pegs, or your memory palace.
Remember the list for the Peg method? Those pegs-images are ready made images that you should memorise before hand, so that you can memorise other information by pair-linkıng the two together.
Associating Numbers, Words, Pictures Names, Cards, and Everything Else In Between
Numbers: To memorise numbers we associate the number digits with images. For example 00: Eggs | 01: Shield & Spear | ..
We use a number system to memorise numbers such as The Shaper System, The Major, Or The Dominic System.
Words: To memorise words we associate each word with related images. For example; Bulgaria: Bull | France: Eiffel-Tower | Iceland: Ice-Cubes | ..
We use a word system to memorise words either by; Word by word with or without a memory palace, Pair-Link two words together, Chain-Link them all.
Pictures: To memorise pictures we pair-link each image with a known peg image. We use image system to memorise images.
When you want to memorise 10 different pictures, and you want to memorise those pictures in the correct order;
Simply add the number shapes from 1-10 into each picture by Pair-Linking with an action. Mentally walk back and you’ll remember them all.
Names & Faces: To memorise names we associate the names with images. We use a names system to memorise names.
When you have a Face & name to memorise; Think of an image that sounds like the name, and mentally attach that image to the face.
If & when you can’t find one, use the Shaper System Alphabet Pegs with a mixture of Vowels & Consonants”, attach them to the face to remind you of the name.
Cards: To memorise cards we associate all cards into images . We use a card system to memorise cards.
Most people who likes to memorise cards uses a Person Or Objects Image for each card in the deck. This is what’s knowns as “1 Card System” which is a single image for a single card.
A 1 Card System simply places each card-image into a memory palace mentally. A 1 card system can be a “PA: Person Action” which is a method to memorise 2 cards at a time.
A 1 Card System is also used as “PAO: Person Action Object” which is a method to memorise 3 cards at a time.
A Two Card System would mean that you would assign a combination of two cards into a single image. This is known as “2 Card-System”.
And we associate everything else in between into images.
Everything Else: Each time you want to memorise some new information;
* You first must convert the new information into a list.
* Find a tangible image for each new item on the list.
* Use the correct system to memorise your list.
Associating Images With Number Digits
The Shaper System
To give an idea of how we generate images by way of associations from the list above, it will provide you the methods of associating with the images for the rest of the list.
To memorise Number Digits we use a method of association to generate images known as “Number To Image Generator”.
It’s a good idea to have number digits as a pair from 00-99. This means that you can memorise two digits at a time by generating images that you can use as your pre-memorised pegs.
For example;
Using The Shaper System;
00 = Eggs
01 = Shield & Spear
02 = Dinosaur
03 = Fork
04 = Knife
and this list goes on until
99 = Balloons.
The images from the Shaper-System gives us 100 pegs. We can use these items as pegs storage to pair link information.
Or we simply use them as items that represent all 100 to digit combinations to memorise numbers to however long we like using a memory palace!
The Shaper-System is a ready made system in a box. Meaning; the images, actions, objects, and everything else are all ready to be used out of the box. You don’t need to prepare any images for any of the shapes and pictures for any of the disciplines you would use to memorise information. It’s all ready to be learned, and ready to use. Another good thing with the shaper system is that you will have the ability to edit any of the materials you like to convert it into your own version of the shaper system!
“The Dominic System”, and “The Major System”.
There are two other Number To Image Generators known as “The Dominic System”, and “The Major System”.
The Dominic System is a “Number To Person-Image Generating System” with the number digits from 00-99.
The Dominic System uses the numbers from 0-9 as the base and assigns a letter to each number as follows;
0 – O | 1 – A | 2 – B | 3 – C | 4 – D | 5 – E | 6 – S | 7 – G | 8 – H | 9 – N
So the first two digits would be;
00: OO
Next and so on until 99;
01: OA
02: OB
…
99: NN
This also provides 100 images. Since The Dominic System is a Number To Person Image Generator, we use each digit with the matching initials and find Persons with A Name & Surname.
As an example;
00: OO – Olive Oyl
01: OA – Orlando Anderson
02: OB – OBama
…
99: NN – NiNa
Once you have 100 Persons, you then think of their Actions, and then their prop, such as clothing or an item that carries or uses most of the time.
You then pair link the digits as PA: Person Action.
Here is an example;
00: Olive Oyl is Cooking Spinach.
02: OBama is Giving A Speech.
If you happen to get these four digits to memorise, this is how it would look like when you see;
PA: 00 02: Olive Oyl is Giving A Speech.
Or if it was the other way round;
PA: 02 00: OBama is Cooking Spinach.
The Major System is a “Number To Image Generating System” with the number digits from 00-99.
The Major System uses the numbers from 0-9 as the base and assigns a Consonant-Letter to each number as follows;
0 – s,z | 1 – t,d | 2 – n | 3 – m | 4 – r | 5 – l | 6 – sh, ch, jh | 7 – k | 8 – f | 9 – b, p
So the first two digits would be;
00: ss
Next and so on until 99;
01: st
02: sn
…
99: pp
This also provides 100 images. Since The Major System is a Number To Image Generator, we use each digit with the matching consonant sounds to make a word, and then convert that word into an image.
As an example;
00: ss – Sauce
01: st – Suit
02: sn – Sun
03: sm: Sumo
…
99: pp: Pipe
Once you have 100 images, you then think of their Actions, You then pair link the digits as OAO: Object Action Object.
Here is an example;
00: Sauce (Ketchup)
02: Sun
If you happen to get these four digits to memorise, this is how it would look like, you would imagine something like;
OAO: 00 02: Ketchup Sauce Poured Over The Sun.
Or you would add a person into the scene such as yourself or another person you would use POAO; Person Object Action (Linked with) Object;
and you would imagine something like;
PO AO: 00 02: You/Him/Her Holding A Bottle Of Ketchup Sauce, Pouring It All Over The Sun.
Or if it was the other way round, you would imagine something like;
OAO: 00 02: Sun is Burning The Ketchup Sauce.
PO AO: 00 02: You/Him/Her Holding The Sun and Burning A Bottle Of Ketchup Sauce with it.
You can create a list of the persons yourself, or check out this website “People By Initials” for ideas to create your 100 persons.
3. Using Exaggerated Actions
As you know already that we pair link two images together by an action. And we create a mini-story by pair-linking or chain-linking by those actions. They will be memorable by all means. However, using exaggerated actions will strengthen the story and therefore make it even further memorable.
As an example;
Let’s use an example person as “Superman” for the number digits “00”, His Action as “Flying Into The Object
So we have;
PA: 00: “Superman is Flying”
Let’s now use another person with another action.
PA: 01: “Batman is Punching”.
Now if we get; 00 01 , This translate to PA as;
PA: Superman is Punching
Or the other way round; 01 00
PA: Batman is Flying.
Now let’s use exaggerated actions here to make it more memorable!
oo 01: Superman is Punching while farting! Oh what a terrible odour coming from him! You can hear it with every punch! He is embarrassed!
Or the other way round; 01 00;
01 00: Batman is Flying while Laughing Out Loud. He may have just realised he could fly, but soon drops to the floor all confused!
Adding exaggerated actions to your paired linked mini-stories will certainly make the story much more memorable indeed.
4. Using Exaggerated Emotions
As with using exaggerated actions, we also use emotions to make our stories more memorable. We are made of our emotions, and it’s one of the main reasons why we are by default able to remember more than we think. We use our emotions to make decisions with everything we do through the day. And by the end of the day our brain can remember most of the day’s activities.
We are emotional beings. We can be very Sad, Angry, Stressed, Violent. But at the same time we can be a loving person, full of joy, enthusiasm, laughter, ambitious,
Adding emotions to your stories will double the strength of the paired link mini-story and therefore becomes much more memorable.
As an example;
Let’s go back to Superman and Batman but this time notice their emotions to it.
oo 01: Superman is Punching while farting! Oh what a terrible odour coming from him! You can hear it with every punch! He is embarrassed!
Or the other way round; 01 00;
01 00: Batman is Flying while Laughing Out Loud. He may have just realised he could fly, but soon drops to the floor all confused!
Adding exaggerated emotions to your paired linked mini-stories will certainly make the story much more memorable indeed.
In fact you may sometimes have difficulty forgetting it for a good while, unless otherwise you practice spaced repetition which is the last subject I will cover.
5. Remember To Practice
Visualisation is a skill you can learn by simply practicing it over and over.
Using you 5 senses to learn every image you generate, along with adding exaggerated actions & emotions will double and triple your imagination.
Learning is the key to applying the methods successfully. Practice is the key to memorising successfully.
12. SPACED REPETITION
Spaced repetition is where you would have to review your system’s images, pegs lists, memory palaces, and the subjects you have memorised over a period of timed intervals.
- Review your system’s images for Numbers, Words, Pictures Names, Cards, and Everything Else
- Review your Peg-Storage images for storing information with using the lists of your peg method.
- Review your memory palaces each with room by room, and all the items at its belonging locations.
- Review your subjects you have memorised such as The Presidents, History Facts, Dates, Speeches, and everything else you want to keep in your long term memory.
- Mentally review all of the above at timed intervals.
Timed Interval Reviews For Long Term Memory
After you have memorised your subject’s list, you will have to mentally review your steps again a few times over a period of time if you want to keep it memorised for long term or permanently.
The recommended time interval for reviewing your subjects again is as follows;
* Review after 10 minutes
* Review after 1 hour
* Review after 8 hours
* Review in 24 hours
* Review 1 week later
* Review 1 month later
* Review again in 3 months
* Review again in 6 month
* Review again in 12 months.
If you follow the timed intervals to review all the long term memory materials, you’ll have them programmed into your mind forever!
And you will have the ability to memorise almost anything you like, at any time you like.
Spaced Repetition Tools You Can Use To Review Your Materials.
* Your PC or Laptop is your best friend for your reviews! Most of the images and notes has to be saved on your PC or Laptop’s hard-drive
* Spreadsheets are very helpful to review your materials.
* Anki can help you setup your materials in a flash-card format. Click Here To Download from Anki’s website.
* Mnemosyne is another platform you can use to save your materials for reviews. Click Here To Visit The Site.
* Art Of Memory Software (Recommended) is a brilliant software for saving and reviewing. Click Here To Visit The Software.
Part Three: The Shaper System

DOWNLOAD BOTH VERSIONS – FREE!
* The Shaper System Starter Version – Free Full System Download Here.
* The Shaper System Full Version – Free Full System Download Here.
General Background
The Shaper System was developed by a Mnemonist Erol Ozvatan with the initial thought of converting 2 digit numbers and The Alphabet letters from its outline shapes into images that has the impression of a lookalike shape & reflection.
As an example; The image for “19” is an Elephant in the shaper system. This is because the number digits are seen with its outline shape, and reflects the impression of an Elephant with its “Back Tail”, “The Big Ear” and “The Trunk” of an Elephant that looks like “19”.
Another example is “20” which is “Snail”. Again the number digit are seen by its outline shape, and reflects the impression of a “Snail” that looks like “20”.
The Shaper System is used to memorise;
Number Digits | Binary Digits | Playing cards | Images | Words | Memory Palace | Lists | Names & Faces.
Numbers And Images Of The Shaper System From 00-99
The basic Number Shape System generates images from 0-9.
The Shaper System was further developed to generate images from 00-99.
The shaper system is a 2 digit “Number To Image Generator” that generates an instant 2 digit lookalike image from 00-99, totalling 100 images.
With the addition of the basic Number Shapes, a total of 110 images can be used.
See “The Shaper System” – Number Shapes – 00 – 99 for a description and discussion of the techniques.
Here are the Number Shapes Of The Shaper System.
Numbers Shapes 0-9
- 0 – Egg
- 1 – Magic Wand | Lighter
- 2 – Duck | Coat Hanger | Pigeon
- 3 – Lips
- 4 – Knife | Chair
- 5 – Teacup | Measuring Jug (tilt the number to the right)
- 6 – Whistle
- 7 – Axe
- 8 – Woman Dress | Catsuit
- 9 – Boxer’s Glove
Numbers Shapes 00-09
- 00 = Binoculars
- 01 = Shield & Spear
- 02 = Hoover
- 03 = Rabbit
- 04 = Chopping board & Knife
- 05 = Lantern Torch With a Handle
- 06 = Golf Ball & Golf Club
- 07 = Paint Roller
- 08 = Pool Ball – Black Ball with 8 on it.
- 09 = Tennis Ball & Racket
Numbers Shapes 10-19
- 10 = Fat Man | Drum
- 11 = Drum Sticks
- 12 = Needle & Thread | Playground Slide
- 13 = Pregnant woman
- 14 = A guy sitting | Heart – Valentine’s Day | Red Rose | Necklace
- 15 = Man pushing a Disabled Chair | or just a Disabled Chair
- 16 = Man smoking Pipe | Man pulling a trolley
- 17 = Harp | Woodpecker
- 18 = Broom & Snowman
- 19 = Elephant
Numbers Shapes 20-29
- 20 = Snail
- 21 = Dollar sign
- 22 = Pair of High Heels Shoes
- 23 = Swan – Neck-body-tail
- 24 = Alarm Clock (Associated)
- 25 = Santa’s sleigh | (Associated > Santa – Xmas Day – Present | )
- 26 = Watering can
- 27 = Trowel
- 28 = Crocodile
- 29 = Gondola and man
Numbers Shapes 30-39
- 30 = Jellyfish
- 31 = Lips smoking cigarette | Bow & Arrow
- 32 = Teeth | Shark | ( Associated)
- 33 = Seagull | Angel Wings | Lips Kissing
- 34 = Goat with Horns | Sheep
- 35 = Crane Hook
- 36 = Lips smoking pipe
- 37 = Rocket
- 38 = Beetle Car
- 39 = Lips & Party Whistle
Numbers Shapes 40-49
- 40 = Concrete Mixer Truck
- 41 = Man Jet Skiing
- 42 = Horse Head and Neck curve
- 43 = Fish
- 44 = Umbrella ( the second 4 flipped horizontally)
- 45 = Kite & string
- 46 = SeaHorse
- 47 = Chihuahua
- 48 = Pick up Van (8 tilted down as the wheels)
- 49 = Mice
Numbers Shapes 50-59
- 50 = Tractor
- 51 = Pipe Wrench
- 52 = Playing Cards (Associated)
- 53 = Bra
- 54 = Snake and his head
- 55 = Wheelbarrow | 2 Hands High Five (Associated)
- 56 = Forklift
- 57 = Blacksmith Anvil
- 58 = Scooter (8 tilted down as wheels)
- 59 = Bull
Numbers Shapes 60-69
- 60 = Monkeys Tail and Body
- 61 = Fishing Tackle
- 62 = Cat
- 63 = Bee
- 64 = Golf Club & Flag
- 65 = Muscle Arm & Bicep
- 66 = Two Cherries with a leaf
- 67 = Punching Machine
- 68 = Pram
- 69 = Yin Yang
Numbers Shapes 70-79
- 70 = Straw in a cocktail glass
- 71 = Fire Extinguisher
- 72 = Water pump
- 73 = Camel
- 74 = Semi Automatic Handgun
- 75 = Exercise Bike
- 76 = Saxophone
- 77 = Two man Rowing | Two bent legs
- 78 = Shopping cart (8 tilted down as wheels)
- 79 = Axe and Farmer
Numbers Shapes 80-89
- 80 = Baby Dummy
- 81 = Violin and bow | Guitar
- 82 = Woman & Long Hair | Hair
- 83 = Mermaid
- 84 = Bride and Groom (arm) – Bride holding arm with the broom and walking.
- 85 = Girl on a Unicycle | Unicycle
- 86 = Girl blowing a Whistle
- 87 = Frog Eyes & Mouth
- 88 = Weights
- 89 = Snorkel
Numbers Shapes 90-99
- 90 = Ninja Turtle
- 91 = Space suit
- 92 = Lion
- 93 = Butterfly
- 94 = Chef & Knife
- 95 = Squirrel
- 96 = Key & Padlock
- 97 = Old Man & his walking stick
- 98 = Biker with helmet
- 99 = Mushrooms | Balloons
The English Alphabet From A-Z
The Shaper System also provides 26 (or more) lookalike images of the English Alphabet from A-Z.
- A = Peg | Eiffel Tower | Tent
- B = Sunglasses
- C = Banana
- D = Bow | Tongue | Protractor
- E = Comb | Trident
- F = Toothbrush | Crutch
- G = Pacman | Ear | G-Clamp
- H = Step Ladder
- I = Flute | Needle | Stick | Candle
- J = Shinty | Shofar | Alphorn | Hockey
- K – Table [tilted] | Whizzy Ride – Bike | Ballerina Dancing
- L – A Gun with a silencer | Ruler | Allen Key
- M – Spider
- N – Compass [North] | Fence | Mach-Sticks
- O – Bracelet | Tyre | Ring | Ball | Hula Hoop
- P – Flag on a pole | Sword [tilted]
- Q – Magnifier | Tiara | Bicycle Pedal
- R – Pincer | Pliers | Badge
- S – Snake | Hook
- T – Cross | Hammer | T-Ruler
- U – Cup | Horse Shoe | Magnet
- V – Necklace | Ice-Cream Cone
- W – Vampire Teeth
- X – Scissors | Plasters
- Y – Slingshot | Funnel | Wine Glass
- Z – Zebra | Escalator | Spring
How it all got started: When I used persons with the dominic system, most of my persons didn’t have any objects or any actions I could apply. And it was somewhat confusing me when I did, and was taking a long time to memorise. So I tried to mix and match with the major system. The major system is a consonant-letter to digits. Again it was taking me awhile to translate the digits and applying the actions.
However, with the number shapes I could see the images more easily and much faster. I also didn’t have to translate it from dominic letters into persons, or translate it from the major into words, and then to create images, and apply the actions. The process seemed to be a lot of work.
With the number shapes, it was easy, no translation needed.
They are just shapes that look like the digits, or the digits that look like the shapes.
The images I have for the shapes also has their own natural actions, or can be created very easily with paired-linking. So each shape-image does the action to the next, or leaves a clue which reminds me of the first 2 digits. So it’s a kind of a system in a box. The Shaper-System-Spreadsheet is available to download. Ready to use..
To start practising the method, Say the Image and its action Out Loud soon as you see the two digit number, and visualise the image and the action at the same time as you practice.
so when you see 00 for example, you’d say “Eggs, Breaking, Yolk running” out loud and see the eggs in your mind.
01 = You say “Spear Stabbing thru”
02 = You say “Dinosaur, Blowing Burning Fire ”
03 = You say “Fork, Sticking into”
04 = You say “Knife, Cutting”
etc, etc.
Then apply the paired link action.
00 01 – You’d say “Runny Yolk on Spear” (Breaking the Spear)
04 00 – “Cutting the Egg”
02 03 – Burning Fork
01 02 – Spear Thru Dinosaur
After practising it for a few days, it will just jump out at you as an image without the need of saying it out loud 
A lot of the images has their own clue when the action is applied, this means that you wouldn’t necessarily have to see the action or the object, because the clue on the object provides the first 2 digits. For example “30” Is Kissing, and the clue of it is “Red-Heart” image stuck/stamped on the next object. “00” is Eggs, All I see is Runny Yolk on the next object as a clue for the “00”. It doesn’t need the action because of the clue.
It is also used with existing systems such as the Dominic or Major System, or any other independent system.
00 – Superman
04 – Cutting (with a Knife)
02 – Dinosaur
Superman Cutting a Dinosaur (with a Knife)
00 – Superman
02 – Dinosaur (Blowing Burning Fire)
04 – Knife
Superman Blowing Fire On a Knife
You’d of course add “Emotions” to it also wherever you can to make it more memorable.
So superman after blowing fire on a knife, also burning his hands on fire, which is not a great feeling.
The above sample is PAO, but you could simply use PA if you are using Dominic PA system. “Superman Blowing Fire”.
Three Main Benefits Of The Shaper System;
1* It does not rely on the Major Phonetics spelling.
So you don’t have to use any consonants, and then find a word, and then find an image etc. Because it’s a self working system with its objects and its actions.
It’s a system in a box that can be learned in a very short time.
2* It can be learned in almost any language!
For example 19 is an Elephant.
The shape of the Elephant looks the same in all languages. It’s a number to image generator, and the image is the same all round the world
3* It can be used with any existing person or object based system variations, as explained above.
5 Ways To Use The Shaper System Images from 00-99.
1. Number System: Use it for your Number System to memorise any number digits to any length.
2. Pegs-As-Storage: Use all 100 images as pegs to store data. No need a memory palace.
3. Mark The Path: Use a shape for each 5th location in a memory palace to remember the order and the position of the path.
4. Mini-Palaces: Use each shape as a “5 Stop Mini-Palace” with Left | Top | Right | Bottom | Middle
5. Expandable Memory Palaces: Use each image to expand the shaper palace to 500 locations.
You can do this simply by mentally adding each image into each corresponding Background image, and you’ll have a 5 stop Mini-Palace with each room, expanding the palace to 500 locations!
There you have it. Hope you enjoyed this course on your journey to a trained brain.
Read, Learn, Prepare, and Practice as much as you can. It’ll be worth it!
DOWNLOAD BOTH VERSIONS – FREE!
* The Shaper System Starter Version – Free Full System Download Here.
* The Shaper System Full Version – Free Full System Download Here.
DOWNLOAD FILES and LICENCE RIGHTS
The Full Number Shape Version | 2 Digits Number Shape System.
The full version of The Shaper System consist of the following files;
* The Shaper System Images
All 100 Number-To-Shape Images
All 100 Number-To-Real Pictures
All 26 English Alphabet-Letter-Shape To Peg-Images
All 100 Memory Palace Background Images.
All 100 Sample Persons To Change With Your Own.
* The Shaper Memory Palace Desktop App
100 stops journey, with 100 background images, specifically chosen for the memory palace. Expandable to 500 Locations.
The app will load the images of the shaper palace by one by for you to memorise your palace in the correct order.
* The Shaper System | Numbers Memory Practice Desktop App
This is the desktop app with the following functions;
* Ability to change every single image with your own to have the final system of your own!
* Loads the Shaper images for each two digit combination.
* Loads Object + Object as a pair, so you can practice your;
“OO”: Object paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads Person + Objects as a pair, so you can practice your;
“PA”: Person paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads The Shaper Palace that consists of 100 background scenes.
* The Shaper System | Binary Numbers Practice Desktop App
This is the desktop app with the following functions;
* Ability to change every single image with your own to have the final system of your own!
* Loads the Shaper images for each binary combination.
* Loads Object + Object as a pair, so you can practice your;
“OO”: Object paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads Person + Objects as a pair, so you can practice your;
“PA”: Person paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads The Shaper Palace that consists of 100 background scenes.
* The Shaper System | Playing cards Practice Desktop App
This is the desktop app with the following functions;
* Ability to change every single image with your own to have the final system of your own!
* Loads the Shaper images for each two card combination.
* Loads Object + Object as a pair, so you can practice your;
“OO”: Object paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads Person + Objects as a pair, so you can practice your;
“PA”: Person paired with the next Object by its Action.
* Loads The Shaper Palace that consists of 100 background scenes.
* The Shaper System “Spreadsheet”
With All 100 Persons Actions Objects, and more..
This spreadsheet is a self explanatory, ready to use out of the box with the shaper system.
It’s specifically designed to teach and to practice all the sections of the whole shaper system.
It’s also editable so you can edit and or change any of the persons, actions, and the rest of the field to organize it into your own system.
*Practice | Practice | Practice
Once you master this spreadsheet, apply all the principles with at least 1 hour practice a day, and you’ll be on your way to memorise 100s of digits easily, that will help you in many ways during your life as numbers are in almost every part of our everyday life. Have Fun!
ps: You will require to download a copy of “Flash Player for desktops” from Adobe website. Else your apps may not work.
https://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/otherversions/
When the shaper system apps opens, you’ll then see a menu with the levels you can practice.
The Certificate Of Completion Free PSD Design
I have provided the PSD the Photoshop File so you can edit and use it if you teach and want to certify your students.
LICENCE RIGHTS
*Use and Edit For Personal – YES.
*Distribute For Non-Profit – YES – As Unedited Zip.
*Teach For Non-Profit Using The Files – YES – Unedited.
*Add or edit, or remove images For Personal Use – YES.
*Can be used as web or e-zine content – YES – With Written Permission.
*Can Put Your Name As The Author and or The Creator – NO!
*Can change the title “The Shaper System” in any document: NO!
*Can change and use the content of Certificate PSD File – YES. Not for profit.
*Can sell – NO!
*Can be offered as a bonus for products sold – NO
*Can be packaged with products for sale – NO
*May be sold as a standalone product – NO
*Can be added to paid membership sites – NO
*Can sell Resale Rights – NO
*Can sell Master Resale Rights – NO
*Can sell PLR Private Label Rights – NO
*Can sell White Label Rights – NO.
Click Here To Start Your Memory Improvement Training
 DOWNLOAD BOTH VERSIONS OF THE SHAPER SYSTEM & APPS – FREE!
DOWNLOAD BOTH VERSIONS OF THE SHAPER SYSTEM & APPS – FREE!
* The Shaper System Starter Version – Free Full System Download Here.
* The Shaper System Full Version – Free Full System Download Here.
Any Questions
Contact me at https://paolist.com/contact
Thanks and Good Luck!
Erol Ozvatan.